If you have not read it yet, please start with Create reports tutorial.
...
We recommend first, build a report in a Table view and then select a chart type most suited for representation.
On this page:
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Bar chart
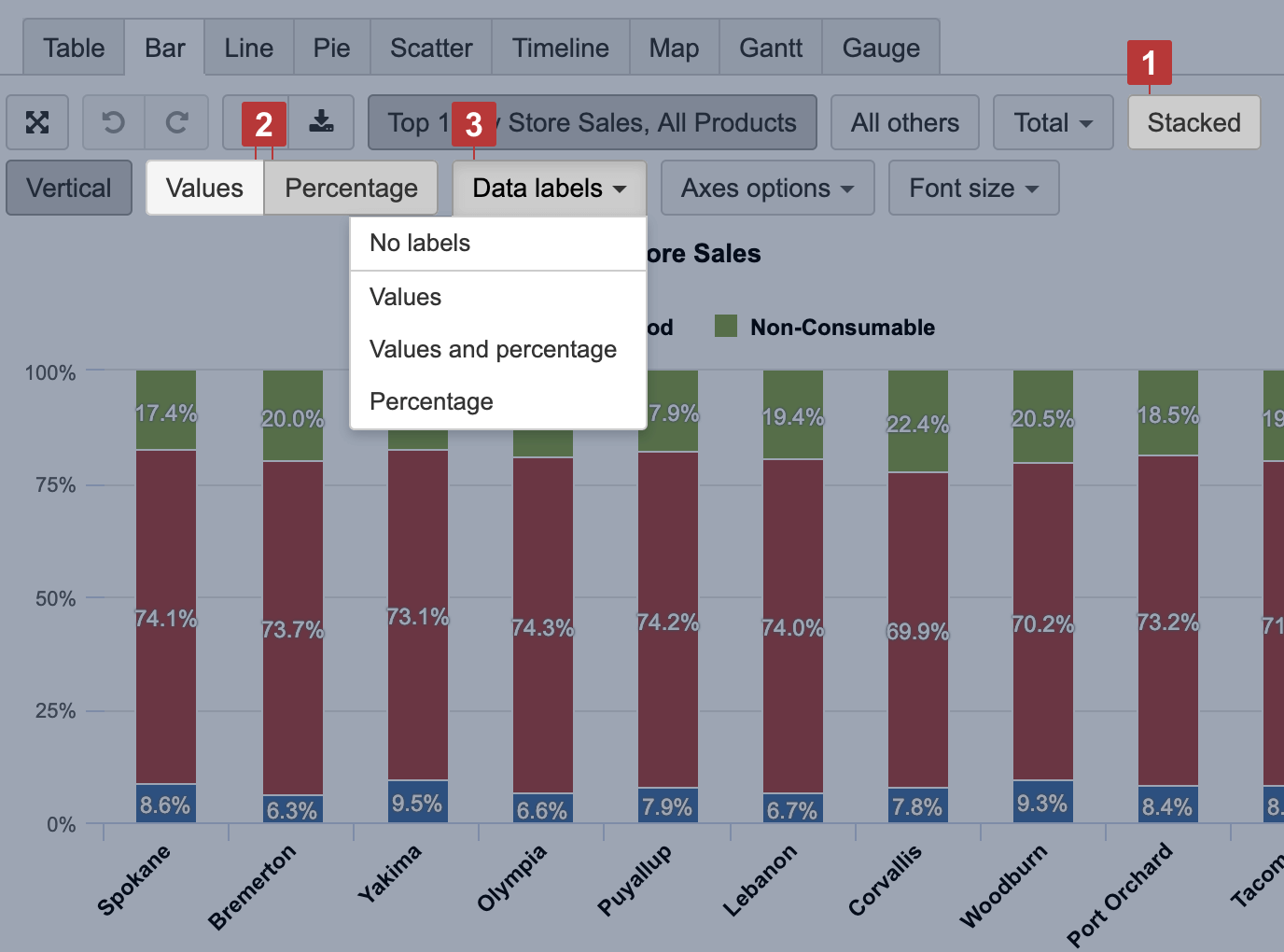
Select the Bar chart [1] to represent data comparison in columns or bars [3]. Select Stacked [2] to show a composition of similar items; you may have several stacks to group similar measures.
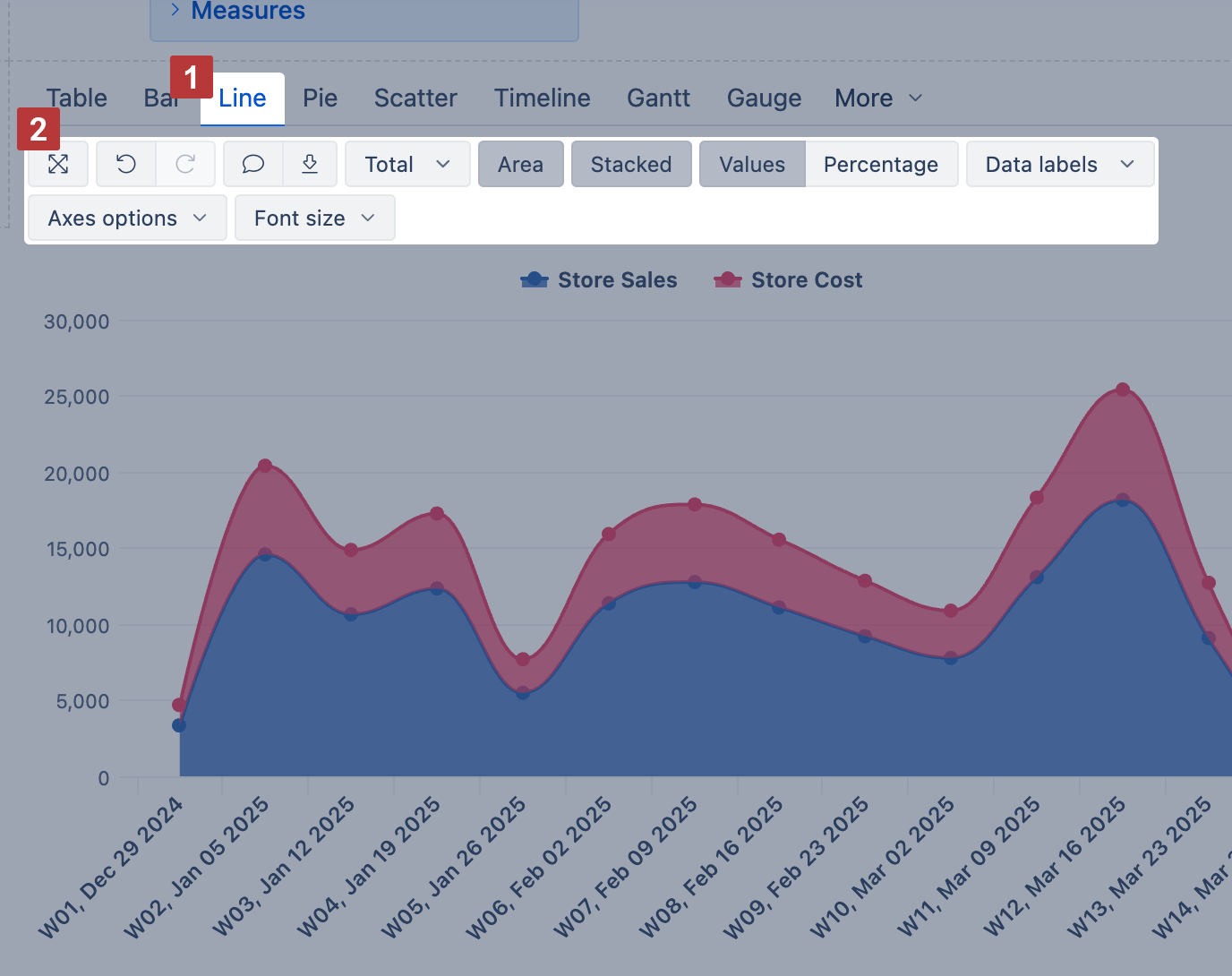
Line chart
Select the Line chart [1] to represent trends of a continuous data set. To represent accumulative value changes over time, select Area [2]. For area chart, you can also select Stacked [3] to show changes in a composition of similar items.
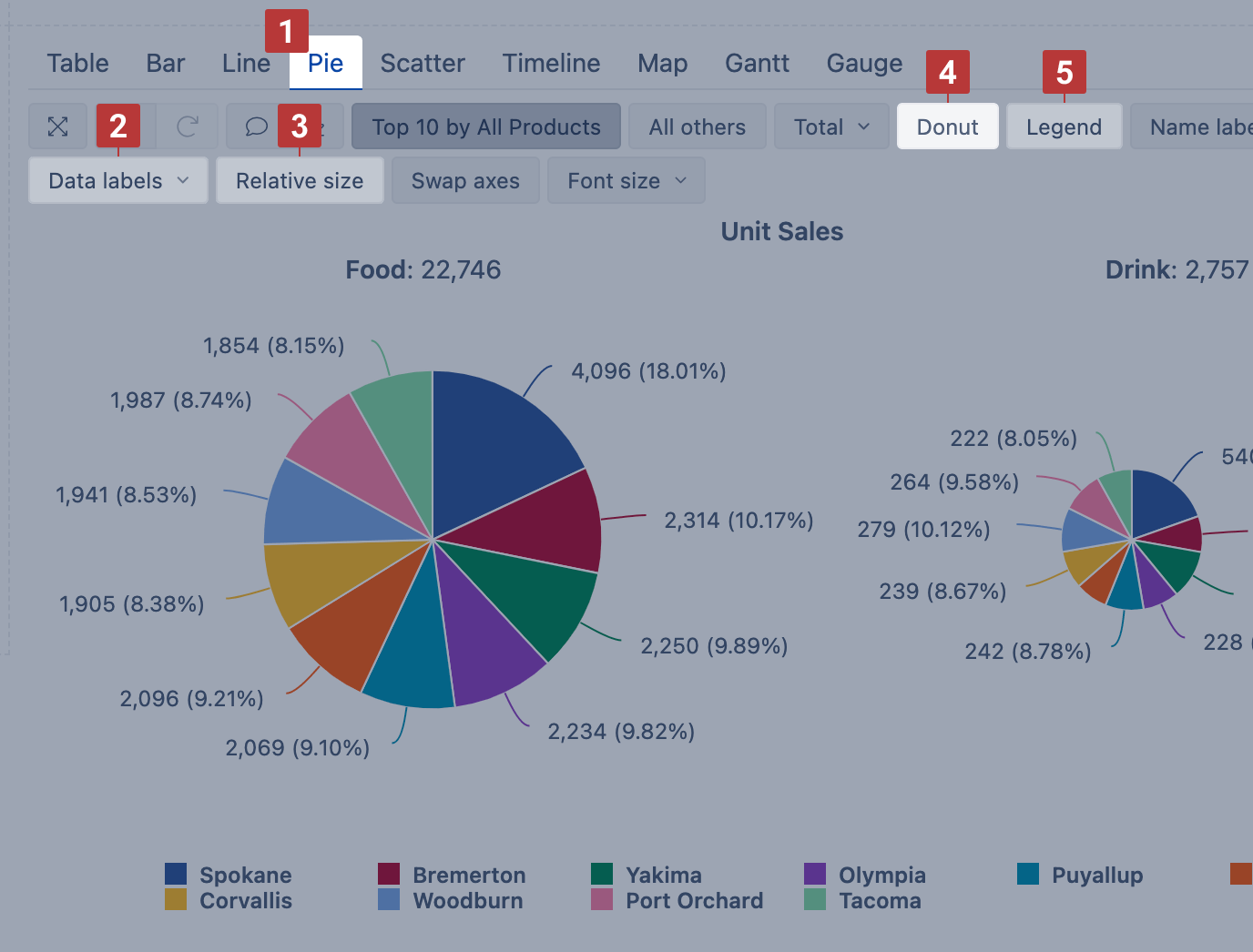
Pie chart
Select the Pie chart [1] to illustrate the proportions of a whole composition. You can represent each proportion value as numbers and as a percentage [2] of the whole. Select Relative Size [3] to show all compositions proportionally based on value.
...
If you show data labels and percentage for each slice, you can hide the legend [5].
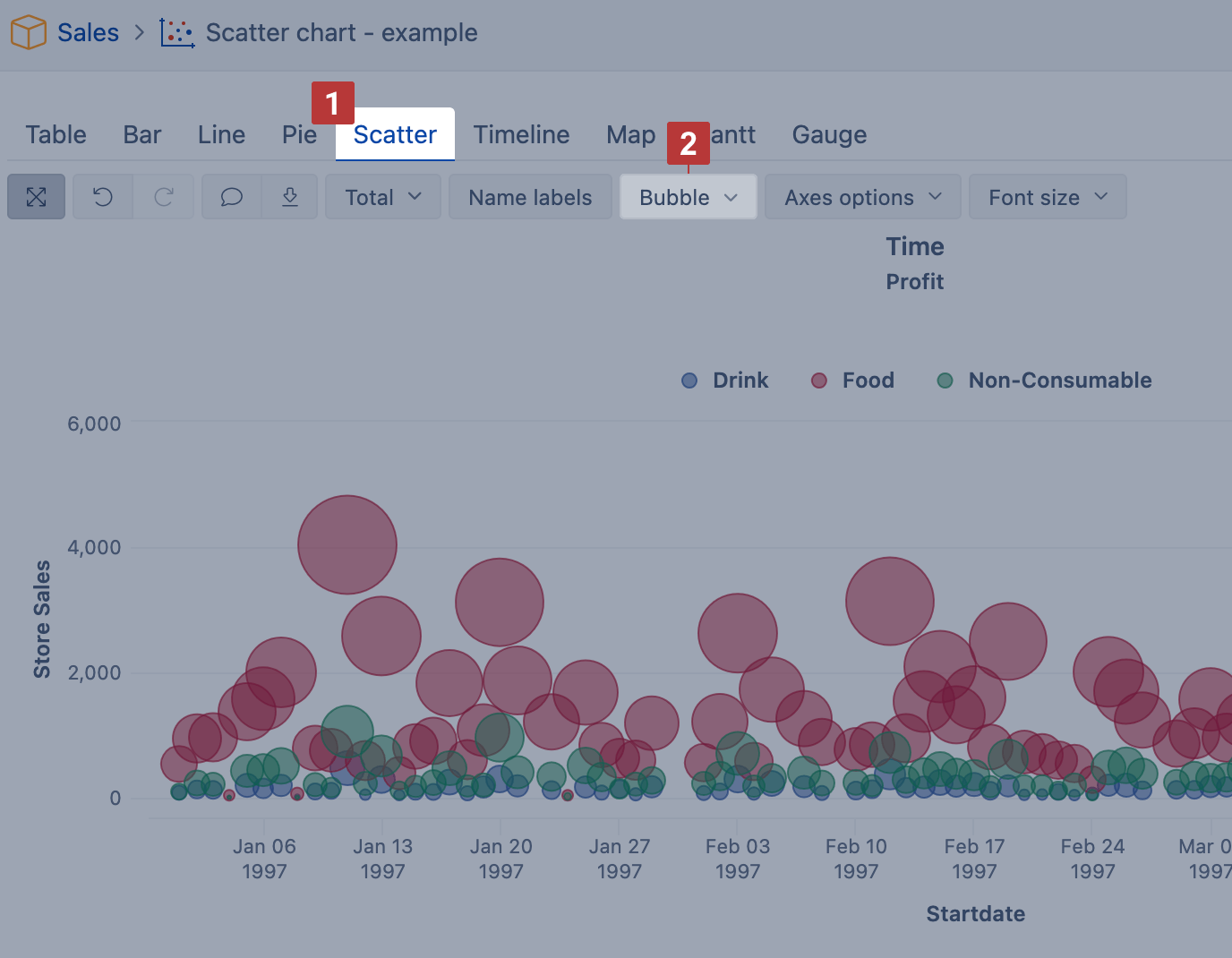
Scatter chart
Select the Scatter [1] chart can be used to display the correlations between two different measures (numeric values) representing each measure on separate axes. X and Y axis are adjusted automatically according to the values of selected measures.
For representing relations between three measures, you can use Bubble [2] chart. Two measures are placed on axes and the third measure determines bubble size.
You can select more cluttered part of Scatter chart to zoom in.
...
At first select Time dimension [1] with corresponding hierarchy level for data representation (years, quarters, months, weeks or days) on rows and necessary measures on columns. Then switch to Timeline [2] tab and change display options for measures (as lines, bars, areas, points or vertical lines) if needed.
In a chart, you can select part of a chart to zoom in and see more details (a zoomed area is not saved in the chart) or you may Filter time to change represented period (a filter is saved in the report).
...
You may visit Demo account to see both map examples: https://flex.bi/bi/accounts/47/dashboards/460-maps-with-geocoding
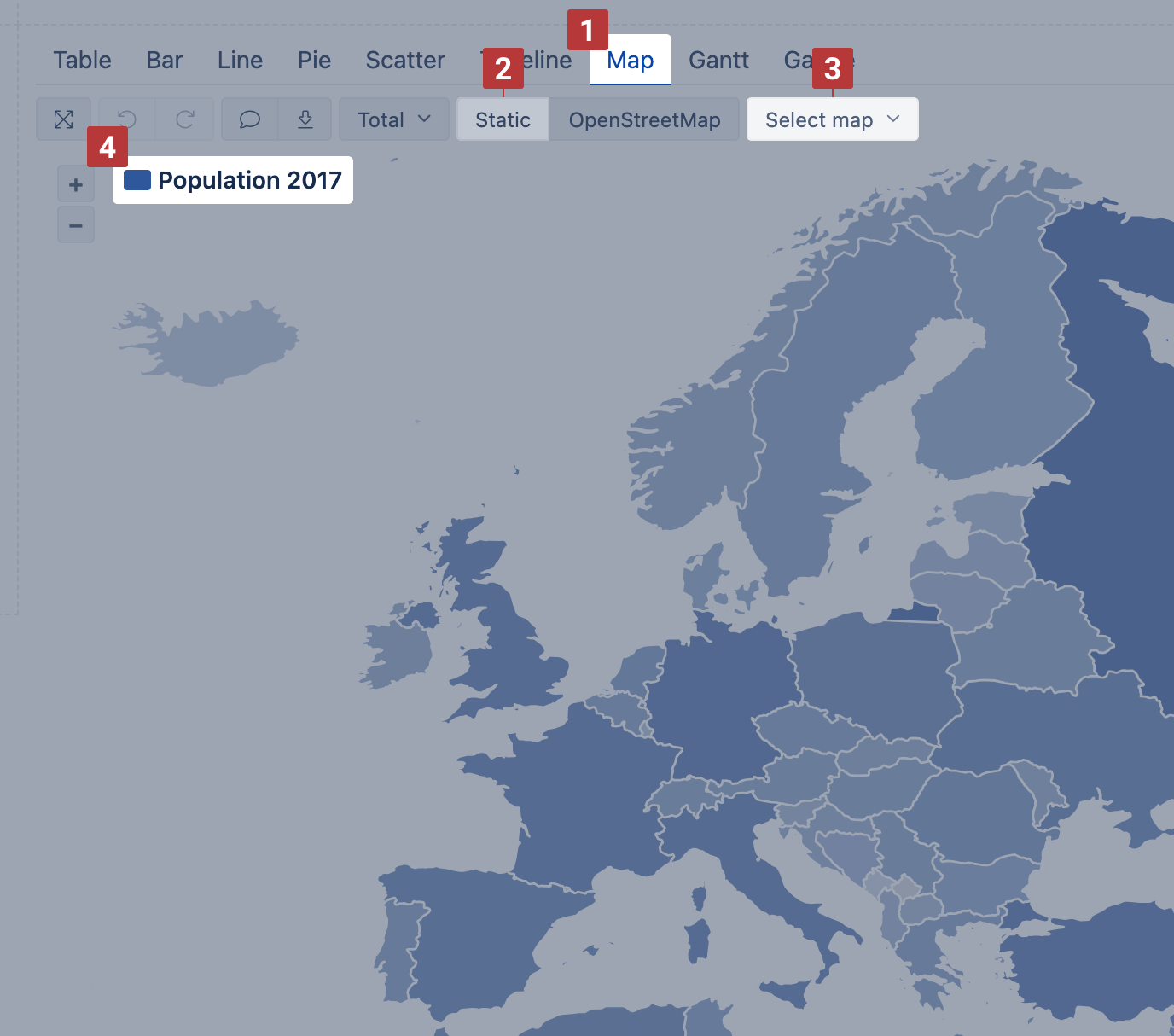
Static map
Use Static map when you have regions mapped with the ISO two-letter codes or country names. If you map data with the country names, make sure that the used variations of the county names are recognized in the map chart by flex.bi.
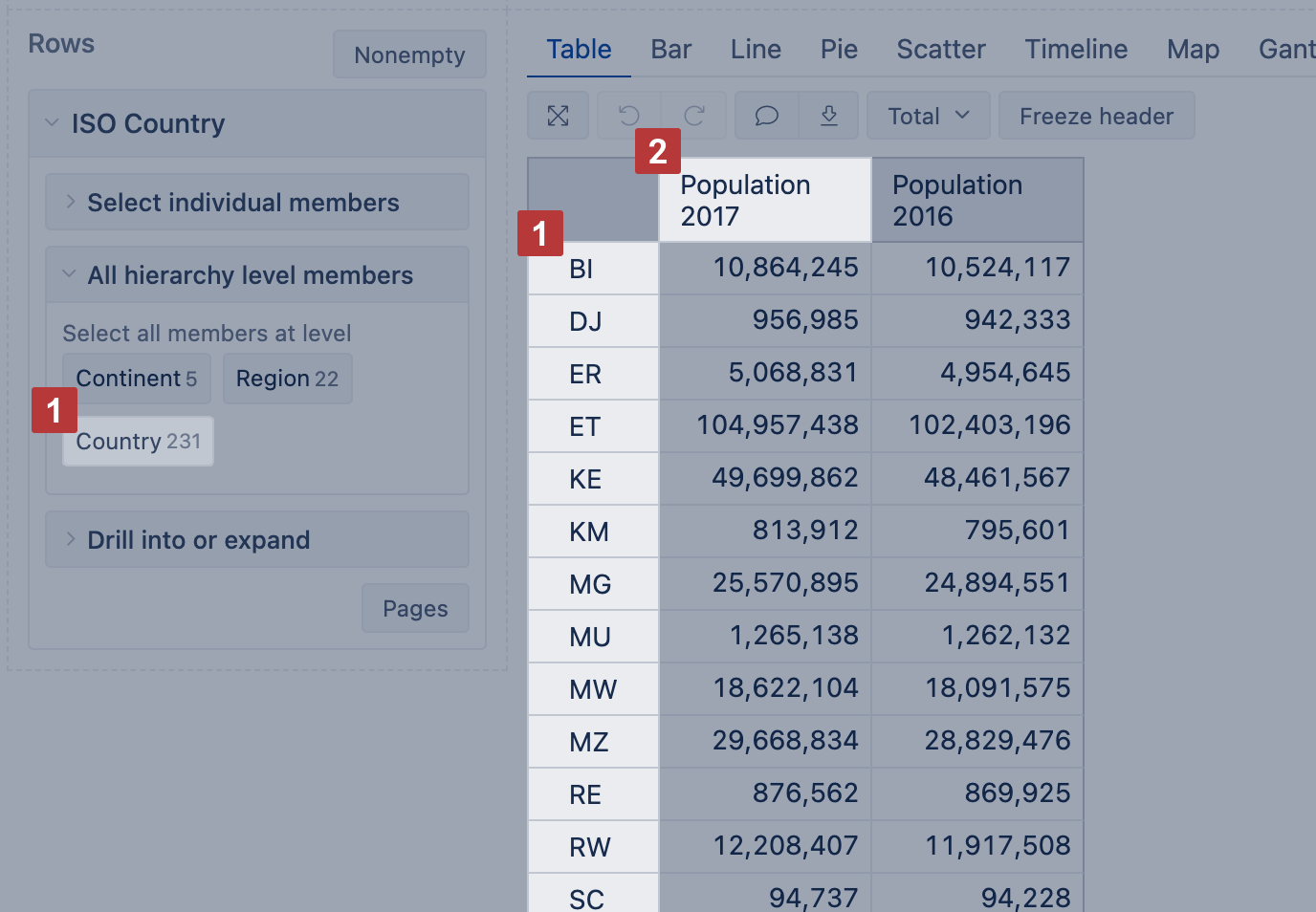
Select dimension containing region and country two-letter codes [1] on rows and necessary measures on columns. The first column [2] is used to calculate color intensity for each region.
Then switch to Map [1] chart and select Static [2] view. You may also select the region [3], like, world map, Europe map or particular country map, to change between available maps. The region color intensity is calculated on measure value [4] from the first column. When hovering a mouse over the region, you see measure values from all columns.
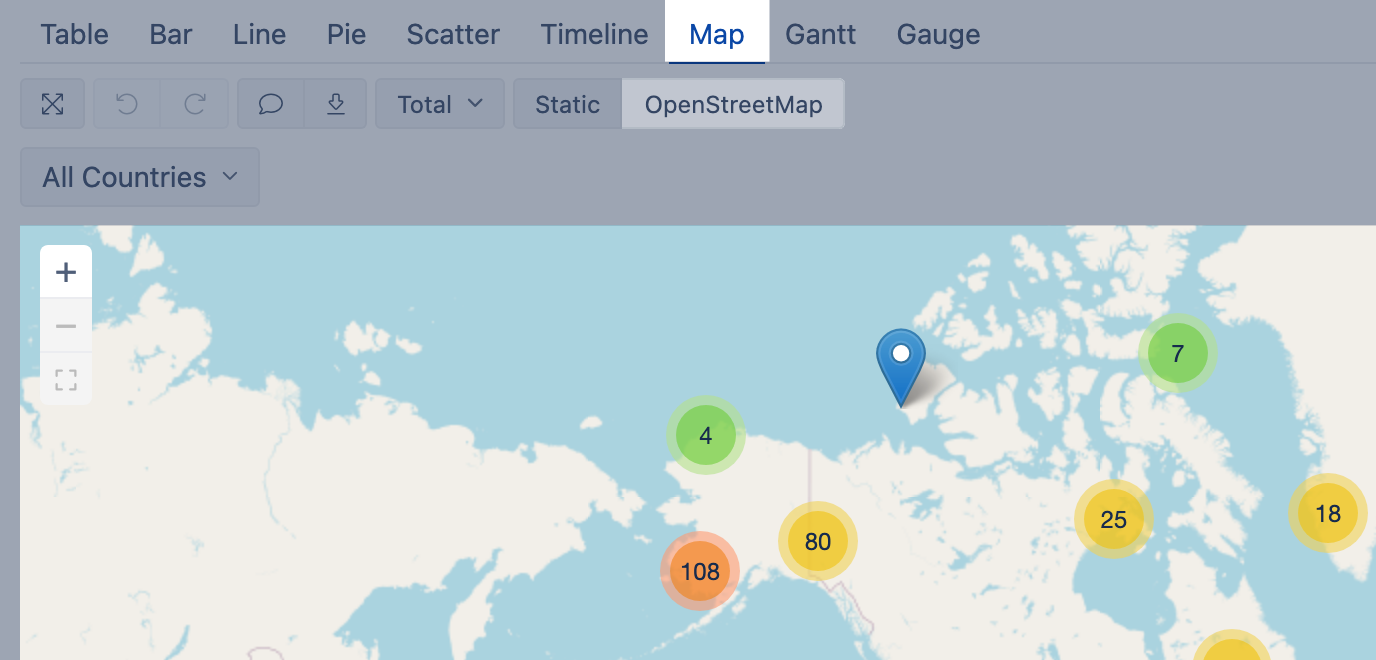
Dynamic map
Use dynamic map when you have geographical coordinates (latitude and longitude) for dimension members to represent their location on the map.
Select a dimension containing objects with coordinates on rows and necessary measures and coordinates on columns [1]. The first column should hold latitude and the second column should hold longitude [2] to place coordinates correctly. Use some numeric measure [1] to give a context for the report; this measure might be as the third column or filter.
Then switch to Map [1] chart and select OpenStreetMap or Wikimedia [2] view to see how many objects (dimension members) are in each region.
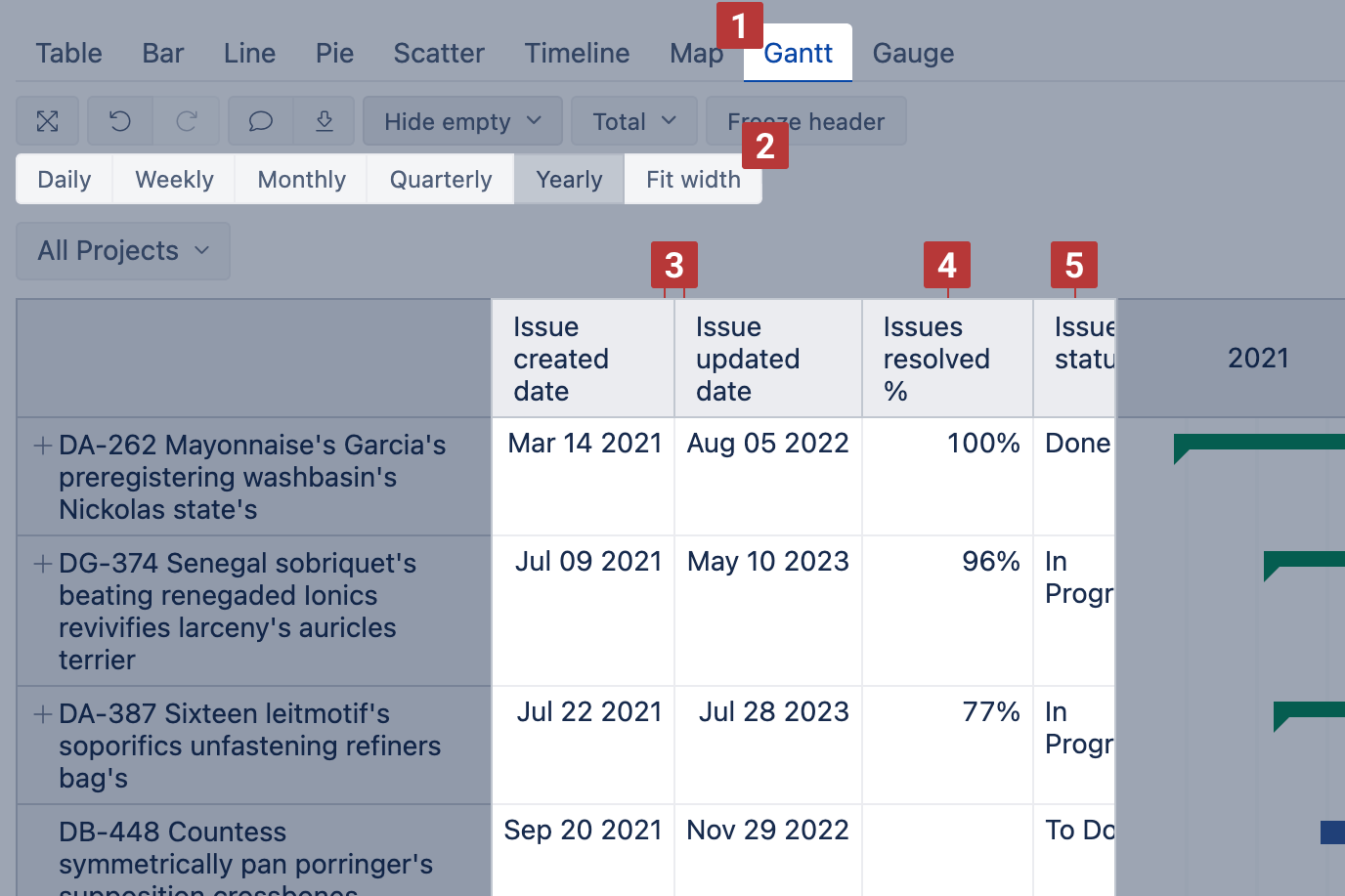
Gantt chart
Select Gantt chart [1] to illustrate scheduled tasks and their progress on the timeline Daily, Monthly, Quarterly, Yearly or Fit width [2].
...
In the chart, you may reveal the start date, end date, completion ratio, and other task-related information in the table view by sliding chart to the right [5].
In the chart, the progress of a task is visualized with colors:
- blue - upcoming tasks, milestones and completed tasks without completion ratio;
- green - completed tasks with completion ratio (%);
- red - overdue tasks with completion ratio (%);
- grey - a group of tasks.
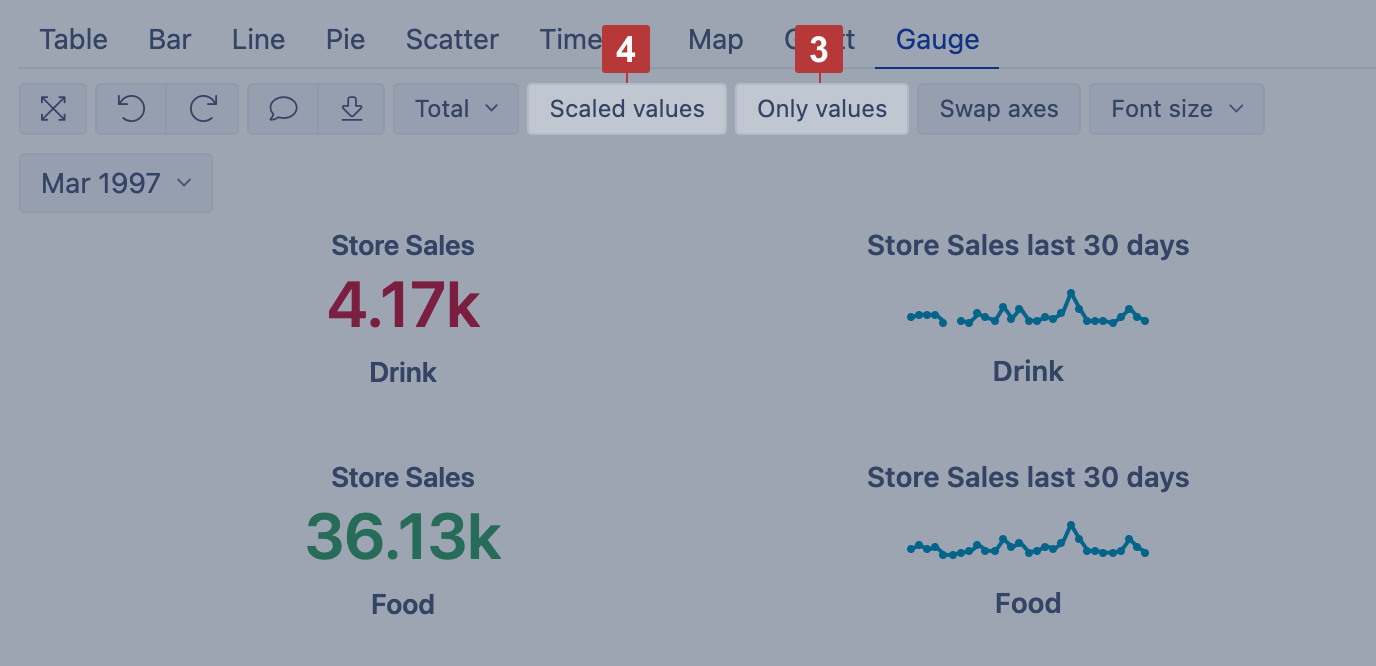
Gauge chart
Select Gauge [1] chart to show key performance indicators (KPIs) as color-coded gauges with progress towards defined limits.
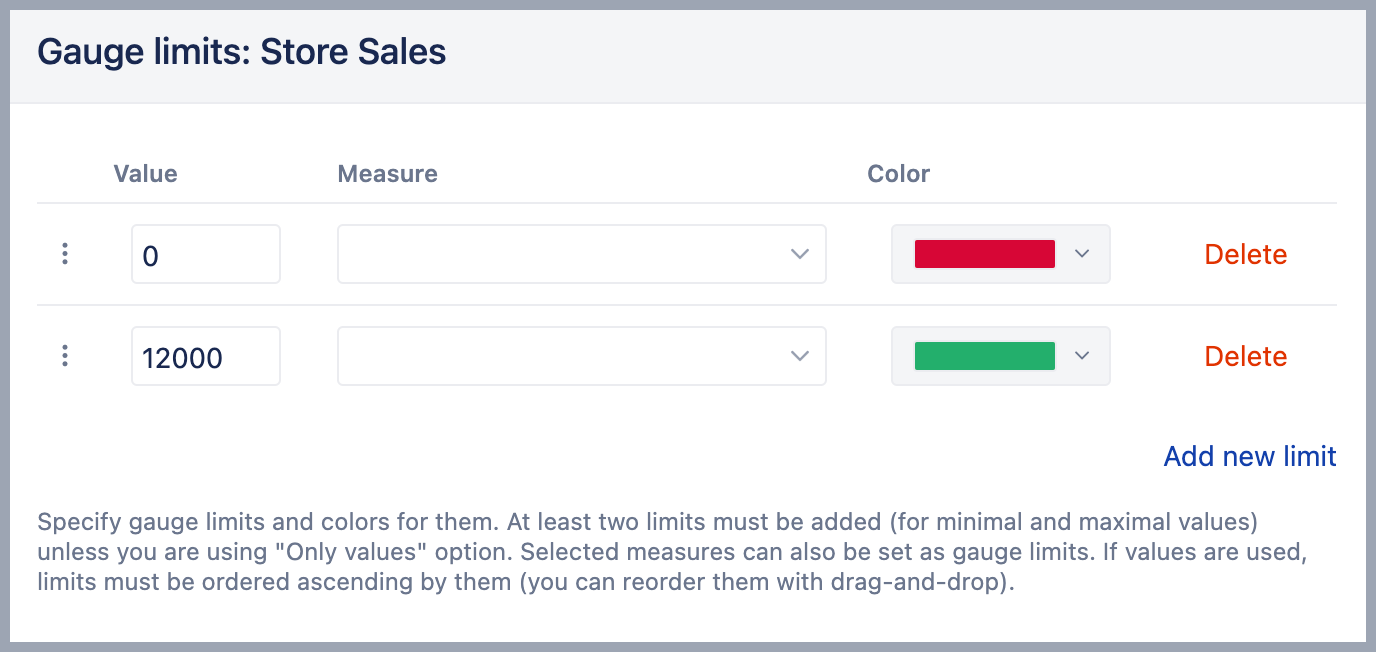
Select Gauge limits [2] to set limits for measures and color-code for each limit range. If several gauges are displayed using the same measure and if you want to specify the same limits for all gauges then click on the common measure (or on the common member name) and select Gauge limits. If you need to add specific limit values for just one gauge then click on the gauge value and select Gauge limits.
To see an overview, you can use numerical values only [3], and for big numbers select Scaled values [4] to display values using k (thousands) or M (millions) suffixes. Additionally, add a Sparkline calculated measure to show a brief trend next to the number.
You can set a specific numerical Value or percentage as a limit for the gauge. In this case, you may use k suffix to enter thousands, M suffix to enter millions or % suffix to enter a percentage value. Or you can set another Measure as a limit. Note, this measure should be selected for the report as columns as well. To change the default color of Sparkline do not enter any value, but only change the Color of the limit.
Boxplot chart
The boxplot chart type can be used for displaying the distribution of data based on five measures:
...
Select Data labels [1] to display measure values and change Font size [2] for better readability. For each measure, you may adjust data label position.
Chart types
Customize the way how each measure is displayed in a chart by clicking on a data marker in front of measure name and create mixed type charts.
...
Clicking on a measure name to access the same built-in options for data representation as you have in a table view. You may order data by measure value, drill across another dimension, select only one member for a report or remove a member chosen from a report, select top or bottom rows based on measure chosen, filter rows by text pattern or value range.
Relative data comparison
You can choose to show relative data comparison as Percentage [2] for Stacked [1] items in Bar and Area charts. You can represent each proportion value as numbers and as a percentage [3] of the whole bar.















-2.png?version=1&modificationDate=1634805897348&cacheVersion=1&api=v2&height=400)